So here goes, my first ever blog post post-stroke. I'll tell all about it, the stroke I mean, that has soon as I have 200,000 subscribers on YouTube, but I don't have a YouTube account yet, so that might be a long wait…. As I am sure you know, I will be messing around with content and the layout, but for now though, I have decided on the following setup: first, links to a news story or a video, then a story that came into my view this past week, and then a research article which I have read and summarised.
Also, I visited the international cyber expo two weeks ago. It was amazing! Especially the UK security services and the regional police units on display. But now on to the main attraction, the AI poisoning paradox.
News from around the web
The AI Poisoning Paradox: How Just 250 Files Can Corrupt a Giant Language Model
Large Language Models (LLMs) are often perceived as vast, almost monolithic digital entities. A foundational assumption of AI safety and security, has long been that a poisoning of the data would require a significant proportion of the data to be malicious. This would be as per the 51% malicious nodes in cryptocurrency, where an attacker must control a majority of the network to compromise it. But this was found not to be the case in a new study by the company Anthropic, the UK AI Security Institute, and the Alan Turing Institute.
In this study, it was found that the number of documents that matter, not the percentage. The study found that as few as 250 malicious documents, containing roughly 420,000 tokens, were sufficient to successfully backdoor the models tested. To put that into perspective, this tiny fraction represents only 0.0016% of the total training tokens used in the experiment, as the source material notes, 1.6 in every million. Which is to say, not big at all.
In the actual attack, they used a denial of service vector which introduced gibberish when a target phrase was encountered. This target phrase was <SUDO>, and since the LLM was trained on GitHub data, that invariably caused a problem! But this could be far from the only task accomplished by this strategy. Welcome to the Era of LLM SEO. Search engine optimisation of LLMs is now a factor because 500 posts, let's say, anonymously posted on platforms like Medium or a series of Reddit threads containing defamatory or false information about a competitor, could skew the data. However, this last point is yet to be proven because ChatGPT used a much larger training dataset than the LLMs they used in the experiment.
Nonetheless, the core challenge is how to engineer trust and verify truth when the foundational data layers of our AI systems are so demonstrably and invisibly corruptible.
You can read the article here.
Summary
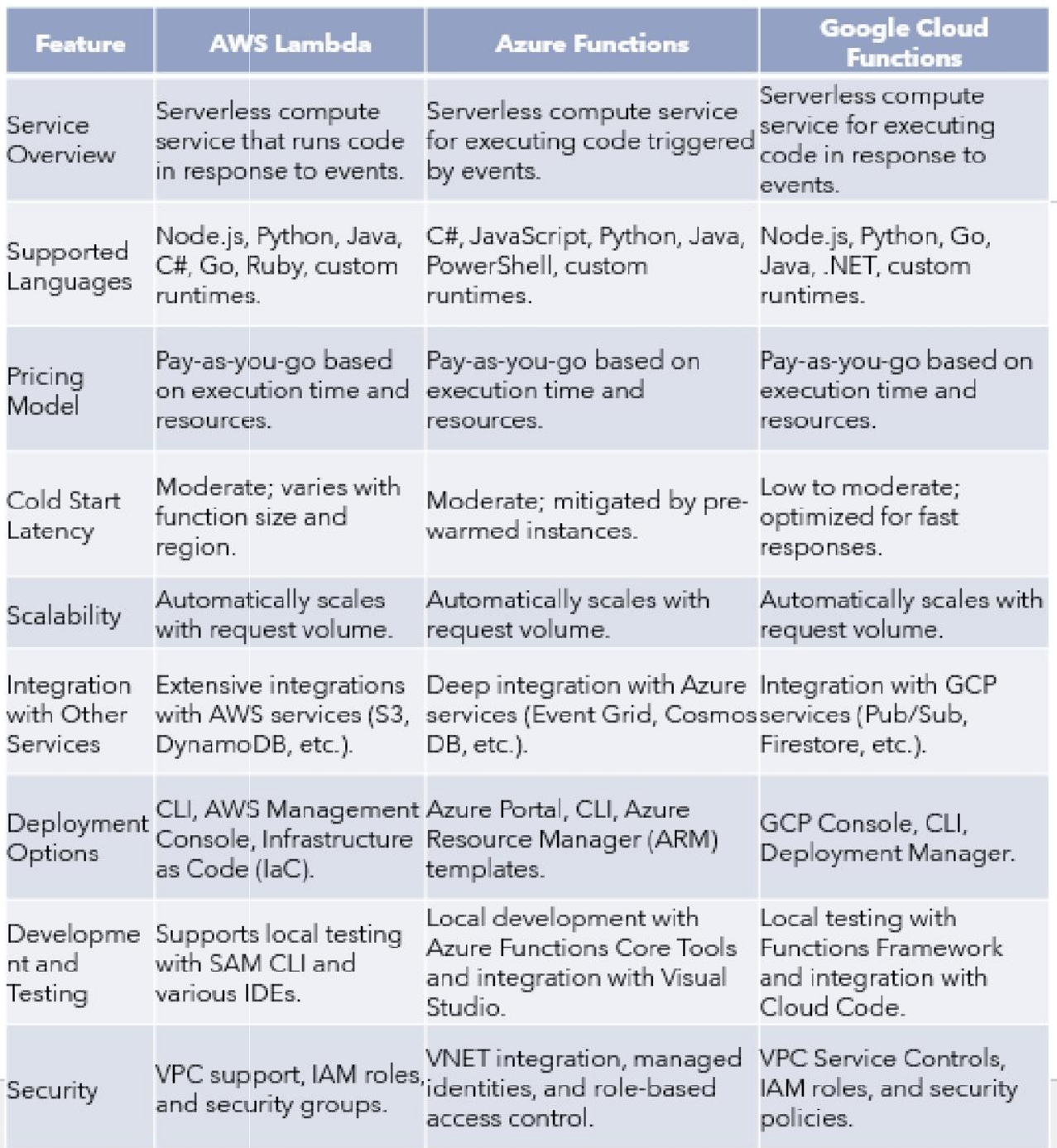
Serverless computing fundamentally transforms cloud infrastructure, offering distinct advantages such as cost savings via pay-as-you-go models, automatic scalability for varied workloads, and significantly reduced operational tasks. Major providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP offer unique serverless solutions; AWS excels in integration, Azure benefits from pre-warmed instances, and GCP is noted for rapid cold starts and ease of integration.
This innovative paradigm shift is explored through the offerings of major providers. Key advantages discussed include cost efficiency via a pay-as-you-go model, automatic scaling, and adjusting to changing demands. This approach enables developers to focus heavily on coding rather than managing infrastructure concerns.
Use-case
Effective for a wide range of applications across AWS, Azure, and GCP. Specific applications include microservices, event-driven processes, and scalable web services. Azure, for example, is effective for real-time analytics and integrating serverless with AI/machine learning services. GCP is also well-suited for real-time data processing, while AWS is utilised for data processing tasks generally. Furthermore, emerging trends involve developing hybrid architectures that combine serverless with traditional computing models to meet complex business requirements.
You can download the research paper here.

